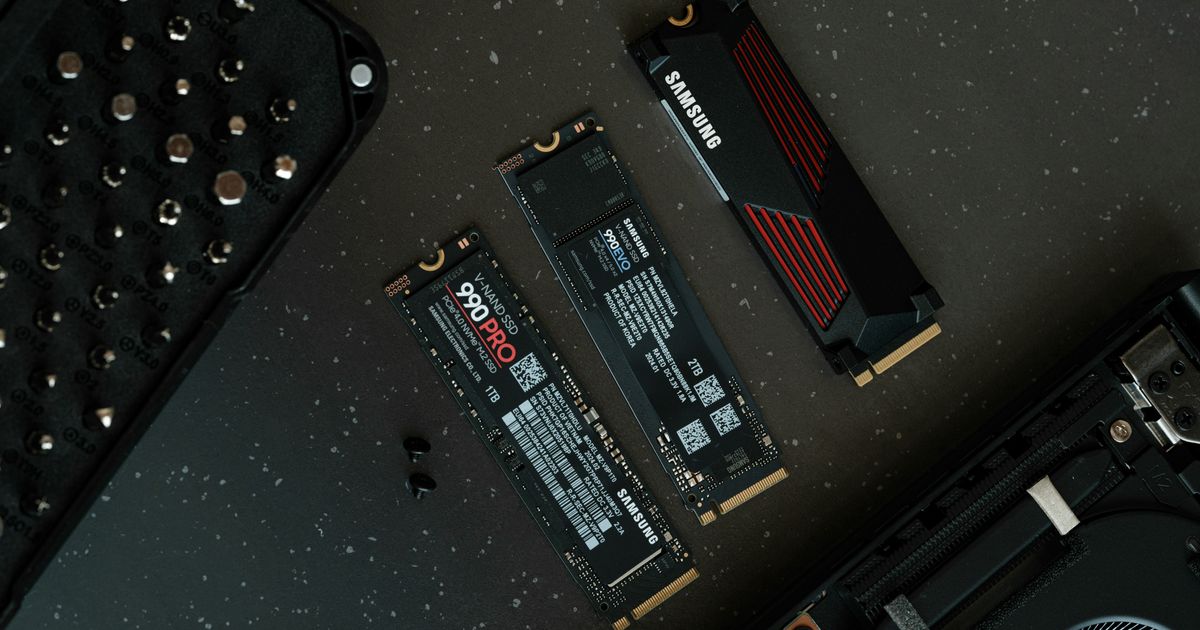
An SSD is a storage device that uses flash memory technology to store data. It offers faster read speeds and quieter operation compared to traditional hard drives.
| Common SSD Specifications |
Currently, the most common SSD specifications are 2.5-inch SSDs and M.2 SSDs.
2.5-inch SSD
This SSD uses the SATA interface, with transfer speeds typically ranging from 500 to 600 MB/s. It's suitable for budget-conscious consumers or as an upgrade for older computers.
Advantages: Faster and more stable transfer speeds compared to mechanical hard drives, with similar pricing.
Disadvantages: Slower transfer speeds compared to higher-end M.2 SSDs, and the physical size is larger.
M.2 SSD
This SSD uses flash memory technology and is installed directly into an M.2 slot on the motherboard, significantly increasing transfer speeds. The latest PCIe 5.0 protocol can reach up to 10,000 MB/s.
Advantages: High-speed transfer rates and no need for additional case space for installation.
Disadvantages: Because of its high transfer speed, an additional heatsink is often required for cooling.

| Choosing the Right SSD Based on Key Factors |
Storage Capacity
Both 2.5-inch SSDs and M.2 SSDs offer similar capacity options, starting at 256GB and going up to 8TB.

Read Speed
2.5-inch SSDs typically have transfer speeds of 500-600 MB/s. M.2 SSD speeds depend on the PCIe version: PCIe 3.0 can reach 3,500 MB/s, PCIe 4.0 can reach 7,000 MB/s, and PCIe 5.0 can go up to 10,000 MB/s or higher.

Case Space
For smaller cases and motherboards (e.g., ITX or compact M-ATX), an M.2 SSD is recommended due to space constraints. For larger cases and motherboards (e.g., ATX or bigger), both 2.5-inch SSDs and M.2 SSDs can be used.

| Important Notes on SSD Installation and Usage |
SSD Length
M.2 SSDs come in different sizes, indicated by a four-digit number. The first two digits represent the width, and the last two digits represent the length. Common sizes include 2230, 2242, and 2280.
M.2 SSD 2230: Suitable for expanding storage in handheld gaming devices.
M.2 SSD 2242: Suitable for expanding storage in ultra-thin laptops.
M.2 SSD 2280: Suitable for expanding storage in desktop computers and gaming consoles.

SSD Lifespan
Since SSDs use flash memory cells, data recovery in case of damage can be costly and may not always be successful. It's advisable to install disk monitoring software like CrystalDiskInfo to check the health of your SSD regularly and to maintain a backup habit.
| Choosing the Best SSD for Your Needs |
When selecting an SSD, it's crucial to consider your needs, budget, and computer specifications. The best choice is always the one that fits your requirements the most.