| What is PCIe? |
PCIe, short for PCI Express, is a widely used bus standard on computer motherboards. It serves as a high-speed interface for connecting various computer hardware components, providing efficient and stable data transfer. PCIe is primarily used to connect devices like graphics cards, SSDs, network cards, and capture cards, among others.
| Key Features of PCIe |
High-Speed Data Transfer
PCIe uses a point-to-point serial connection, meaning each device connected to a PCIe slot has its own dedicated data transfer channel. This allows for significantly faster data transfer rates compared to older standards. PCIe slots come in different versions (e.g., PCIe 3.0, PCIe 4.0, PCIe 5.0), with each new generation offering almost double the data transfer speed of the previous one.
Different Slot Sizes
PCIe slots come in various lengths and lane configurations, including x1, x4, x8, and x16. The number after the "x" indicates the number of data lanes the slot has, which can be thought of as lanes on a highway. For example, an x16 slot offers 16 data lanes, allowing for higher throughput compared to smaller slots like x1, which only has one data lane.
Backward Compatibility
PCIe is backward compatible, meaning a PCIe 4.0 device can be used in a PCIe 3.0 slot, but the device will be limited to the slower transfer speed of PCIe 3.0.
| PCIe Usage and Recommended Slot Types |

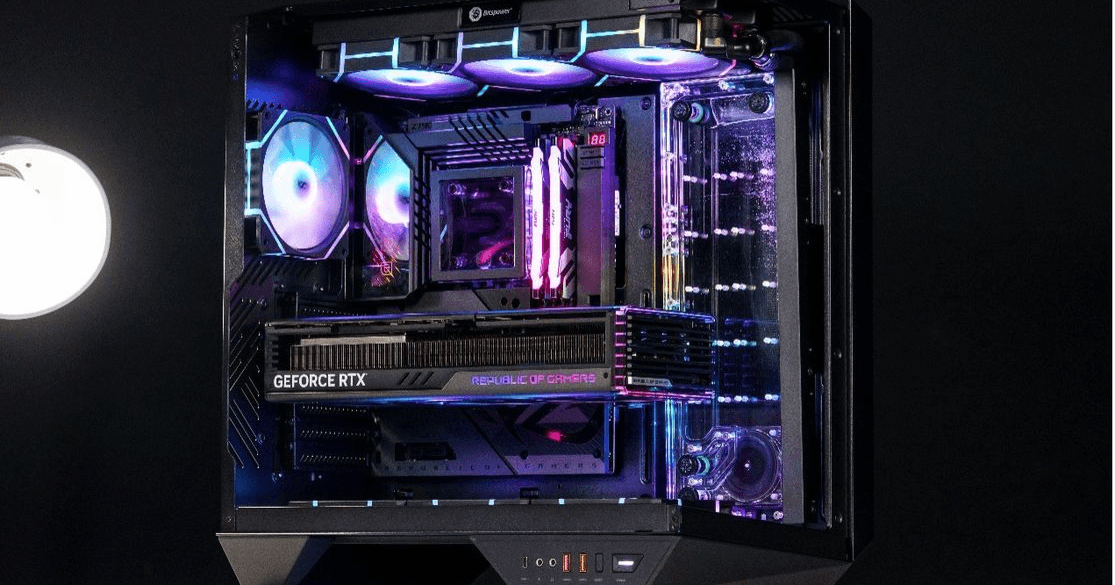
Graphics Card (GPU)
Recommended Slot: PCIe x16
Reason: Graphics cards require the highest bandwidth to handle demanding graphical computations. Therefore, they are typically installed in x16 slots, which provide the best data transfer rates to ensure optimal GPU performance.
Solid-State Drive (SSD)
Recommended Slot: PCIe x4
Reason: SSDs are usually installed in M.2 slots on the motherboard. However, if the motherboard lacks enough M.2 slots, an M.2 PCIe expansion card can be installed in a PCIe x4 slot to fully unleash the SSD's performance.
Network Card (NIC)
Recommended Slot: PCIe x1 or PCIe x4
Reason: While many network cards use USB for hot-swapping, a PCIe network card is typically chosen for more stable and reliable network connections. An x1 slot is sufficient for most network cards, but for higher-speed NICs, a PCIe x4 slot is recommended for improved stability.
Capture Card
Recommended Slot: PCIe x4 or x8
Reason: Capture cards are essential for streamers and content creators, as they handle high-bandwidth video data. To ensure smooth performance, capture cards usually require a PCIe x4 or x8 slot to provide enough bandwidth for high-quality video streaming.
| Important Considerations When Using PCIe |
Bandwidth Compatibility
When choosing expansion devices, ensure that the bandwidth of the device matches the slot's bandwidth. Low-bandwidth slots will limit the performance of high-bandwidth devices.
Physical Compatibility
Ensure that the physical size of the PCIe card is compatible with the motherboard slot. For example, an x1 card can be installed in a x16 slot, but an x16 card cannot be installed in a x1 slot.
Slot Priority
Most motherboards have a slot priority system, meaning some slots are more suitable for high-priority devices like GPUs. To get the best performance, it is recommended to install critical components in slots closer to the CPU, as these slots often offer the best bandwidth and lowest latency.

PCIe slots are critical for expanding and enhancing the functionality of your computer. By understanding the different types of PCIe slots and their recommended uses, you can optimize your system's performance and expand its capabilities to meet your needs. Whether you're upgrading your graphics card, installing an SSD, or adding a network card, choosing the right PCIe slot is essential for maximizing the potential of your hardware.