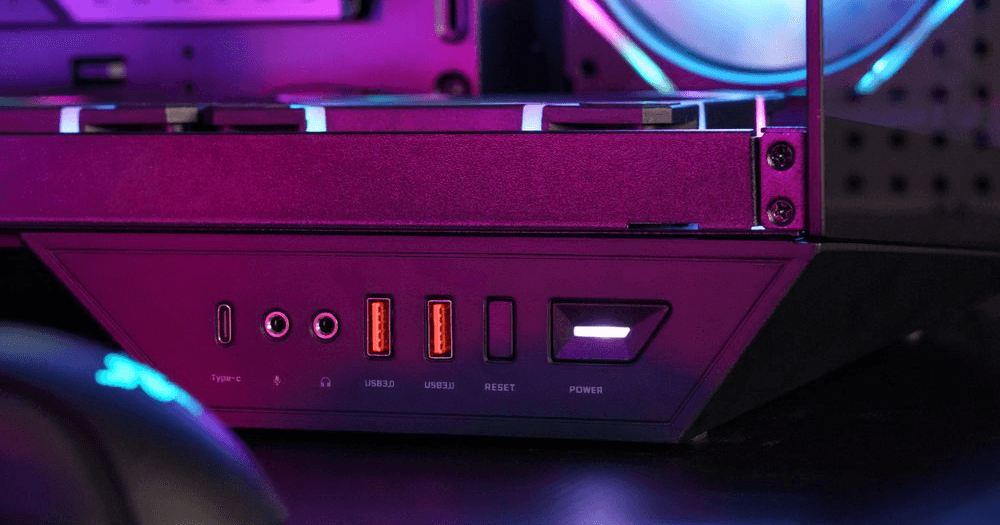
USB, which stands for Universal Serial Bus, is a technology standard for connecting computers to external devices. As data transfer speeds have increased over time, newer versions like USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 have emerged. There are also different connector types such as USB Type-A, Type-B, and the latest USB Type-C, which is oval-shaped and reversible. USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 Type-A connectors are standard on most cases and motherboards. But how can you tell them apart? Let’s break down the key differences:
1. Data Transfer Speed
USB 2.0
Maximum Transfer Speed: 480 Mbps (60 MB/s)
Ideal Use: Connecting devices like mice and keyboards for everyday tasks. USB 2.0 is suitable for low-speed peripherals that don’t require high data transfer rates.
USB 3.0
Maximum Transfer Speed: 5 Gbps (625 MB/s), roughly 10 times faster than USB 2.0.
Ideal Use: High-speed data transfers such as external drives, flash drives, and other storage devices. USB 3.0 is perfect for situations where large amounts of data need to be transferred quickly.
2. Port Color
USB 2.0:
Ports are typically black or white.
The connector has 4 pins arranged in a single row.
USB 3.0:
Ports are usually blue, which helps differentiate them from USB 2.0 ports.
The connector has 9 pins in two rows—5 on the top row and 4 on the bottom row. This physical distinction makes it easy to identify USB 3.0 ports.

3. Connector Style and Compatibility
USB 2.0:
The standard Type-A connector is square-shaped.
Backward Compatibility: You can plug a USB 3.0 device into a USB 2.0 port, but the transfer speed will be limited to USB 2.0’s slower speeds.
USB 3.0:
Also uses the Type-A connector, which looks identical to USB 2.0's Type-A.
Backward Compatibility: USB 3.0 ports are backward compatible with USB 2.0 devices, but the data transfer speed will be capped at USB 2.0 rates.
4. Data Transfer Channels
USB 2.0:
Uses a single channel for data transfer.
Supports one-way data transfer at a time, meaning it can only send or receive data, but not both simultaneously.
USB 3.0:
Supports dual channels for data transfer.
Capable of bi-directional data transfer, meaning it can send and receive data at the same time, significantly improving overall transfer efficiency.
Conclusion
USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 are two distinct data transfer standards, with the main difference being the data transfer speed. USB 3.0 offers a much faster transfer rate, making it ideal for devices that require quick data handling, such as external storage devices. When purchasing a computer case, it’s important to consider the USB I/O ports, as they will directly impact your experience with peripheral devices.